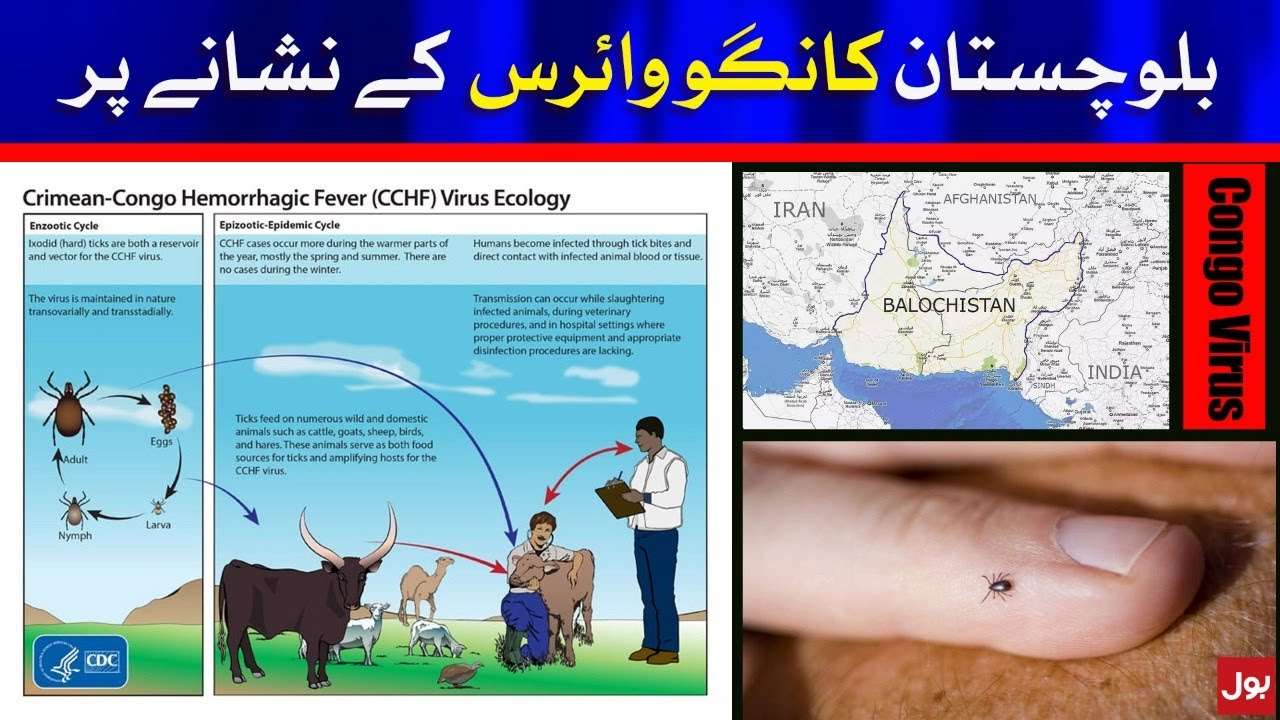
Nevertheless, the alarming rate at which healthcare workers in Balochistan have fallen victim to the virus raises profound questions regarding the adequacy of infection control measures and the accessibility of protective gear. Prompt attention to these concerns is imperative to safeguard the brave individuals risking their lives in the service of others.
Additionally, authorities must join forces with their counterparts in Sindh to expedite safe patient transfers through air ambulances. The challenges brought about by the Congo virus outbreak in Balochistan are both disconcerting and urgent.
The toll of 20 lives lost this year is a stark reminder of the gravity of the situation. Among these unfortunate casualties was a dedicated doctor, racing against time to reach Karachi for treatment. Disturbingly, out of the 200 individuals suspected of being infected, 73 have tested positive for this perilous tick-borne virus.
This outbreak has had devastating consequences, with 12 healthcare professionals now undergoing treatment in Karachi, and the condition of four doctors described as critical.
Situation of PORT CITY
Fortunately, the port city of Karachi has so far remained untouched by this deadly contagion. Nevertheless, the rapid transmission of the infection among healthcare workers in Balochistan serves as a wake-up call, underscoring the urgent need for improved infection control measures and the availability of protective gear.
The severity of CCHF cannot be overstated, as it can result in fatalities in up to 40% of cases. Given the absence of a vaccine to halt its spread, there is a pressing need to focus on public awareness and preventive measures. Those engaged in the livestock industry must be educated about the associated risks of the virus to reduce the likelihood of transmission from ticks to humans and animals to humans.
They must also adhere to strict protocols, including wearing appropriate protective clothing when handling animals, using approved acaricides on their attire, and regularly inspecting themselves for ticks.
The transmission of the virus from human to human can be effectively controlled by promoting social distancing and the avoidance of close contact with infected individuals, emphasizing the importance of hand hygiene, and ensuring the availability of protective equipment in healthcare settings.
Imperative for the government
The government must act swiftly to contain the virus, safeguarding the well-being of healthcare professionals, and ensuring the safety of the public. While certain measures, such as the temporary ban on private slaughterhouses in densely populated areas, have been implemented, time is of the essence, and the lives of healthcare providers and the wider community hang in the balance.
The seriousness of CCHF, with fatality rates as high as 40%, necessitates the expedited development of a vaccine to curb its spread. Until such a vaccine becomes available, the focus should be on raising public awareness and implementing preventive measures. Those involved in the livestock industry must be educated about the risks associated with the virus to reduce the risk of tick-to-human and animal-to-human transmissions.
They should strictly adhere to protocols, including the use of protective clothing when handling animals, the application of approved acaricides to their attire, and regular self-inspection for ticks. Human-to-human transmission can be effectively controlled by promoting social distancing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, enforcing rigorous hand hygiene, and ensuring the availability of protective equipment in healthcare settings.
The government must act swiftly to contain the virus, protect healthcare professionals, and ensure public safety. While certain measures, such as the temporary ban on private slaughterhouses in densely populated areas, have been implemented, time is of the essence, and the lives of healthcare providers and the broader community hang in the balance.